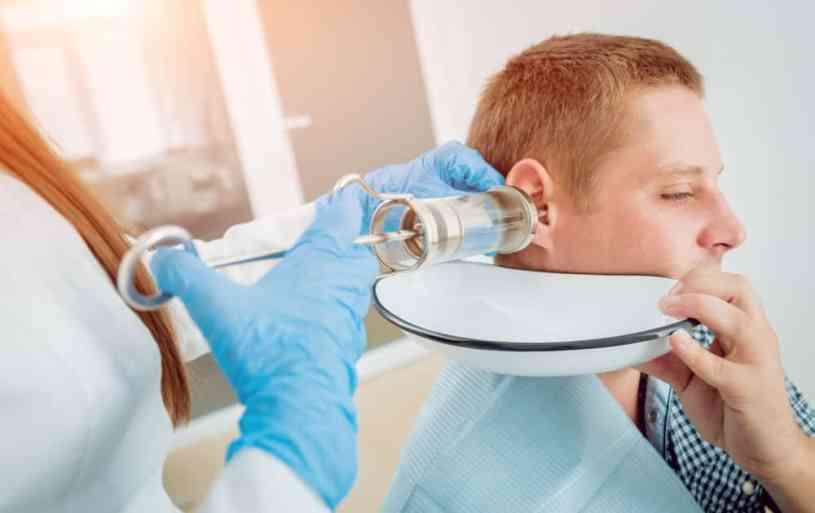
The easiest and safest way to get rid of excess earwax is to see an expert. Ear syringing services should be offered by an accredited and trained professional. Your body naturally cleans the earwax. However, if your body produces excessive earwax, you might experience difficulties in hearing. Earwax buildup can also cause ear pain, dizziness and impaired hearing. In case this happens, getting a checkup is important to prevent other issues with your ear health. Ear syringing is a technique used to remove ear wax by pushing water into the ear canal to remove the ear wax. Despite the procedure being successful, there can be complications and side effects if not properly done. This can cause impacted earwax and ear infections.
Why is Ear syringing conducted
A medical professional performs ear syringing to remove the buildup of earwax, which causes pain, itching, chronic cough or hearing loss. This procedure is not performed unless there is a buildup of earwax.
What Occurs During Ear Syringing procedure?
Before any syringing procedure is conducted, an audiologist checks inside the ear to confirm that the main cause of your symptoms is foreign materials or earwax buildup and not something serious. After the confirmation, the procedure can now be conducted. An electric pump is squirted gently using the right water pressure into the ear canal to remove earwax. The earwax softens and falls out. After the earwax is gone, your symptoms will improve in a day or two. After the procedure, the professional advises on how to avoid further buildup of earwax.
Is Ear Syringing safe?
There are concerns among medical practitioners that ear syringing can cause eardrum perforation, thus allowing water in the middle of the ear. Through the use of the syringing device, you can minimize the risk. Using water at room temperature is recommended instead of too hot or cold, which can cause dizziness.
The Risks and Side Effects
Some people should not undergo the syringing procedure as they can have a higher risk of damage and eardrum perforation. This includes people with otitis externa and those with a history of middle ear disease, eardrum surgery, ear damage and radiation therapy of the Ear. Some possible side effects of syringing include otitis externa, dizziness, middle ear damage and perforation of the eardrum. If an individual experiences symptom such as dizziness, nausea and sudden pain, they should stop the procedure immediately.
Conclusion
Ear syringing is an effective method for earwax removal for individuals with earwax buildup. Excessive earwax can cause hearing loss. However, an individual can make syringing kit at home, it’s always safe for the procedure to be carried out by a doctor. If you don’t prefer your ears syringed, there are other methods of removing wax. Other methods include softening oil such as mineral oil, hydrogen peroxide solution or salted water to drain the wax naturally. Despite this, the best treatment for excessive ear wax is to have a professional examine them and get syringed if necessary.